Difference between revisions of "User:WikiSysop/Information Model"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<div style='font:11pt fixed;line-height:120%'> | <div style='font:11pt fixed;line-height:120%'> | ||
== An Emergence Epistemology for Modern Ontologies == | == An Emergence Epistemology for Modern Ontologies == | ||
On the heels of recent evolution in mathematics and astronomy, physics, biology, social sciences, and cognitive research, a new approach to the process of information modeling is | On the heels of recent evolution in mathematics and astronomy, physics, biology, social sciences, and cognitive research, a new approach to the process of information modeling is needed to support widely common cross-domain requirements, that is, this article proposes a candidate Standard Ontology Model (SOM). | ||
===Motivation=== | ===Motivation=== | ||
Presently ontologies are built using approaches first typified by the Formula Translating System (FORTRAN), and are thus based on essential notions of "data structures" as proxies for operands to an algebraic formula; "routines" being a particular functional formula; and "return values" being the specific knowable output of the formula. The generic formula, <i>y = f(x)</i> (where "y" <u>is equal to</u> "f" upon "x"), exactly maps to the widespread Input-Process-Output model underpinning many methods; it is aptly descriptive to consider the Algebraic Formula the <u>epistemology</u> used to fashion many ontologies. | Presently ontologies are built using approaches first typified by the Formula Translating System (FORTRAN), and are thus based on essential notions of "data structures" as proxies for operands to an algebraic formula; "routines" being a particular functional formula; and "return values" being the specific knowable output of the formula. The generic formula, <i>y = f(x)</i> (where "y" <u>is equal to</u> "f" upon "x"), exactly maps to the widespread Input-Process-Output model underpinning many methods; it is aptly descriptive to consider the Algebraic Formula the <u>epistemology</u> used to fashion many ontologies. | ||
However if success of ontologies is judged by their fruits, the Formula paradigm appears to have produced representations of reality that are not being used to any depth, by anyone, clearly for the principle the ontologies being promulgated have no bearing upon the actual models being developed, and tested, by a data scientist most concerned with alternative theories of '''''interaction and evolution''''' within their domains. The core issue is no public domain ontology exists to structure the problems being solved by data scientists, meaning a scientist's use of today's public ontologies is meaningful primarily as | However if success of ontologies is judged by their fruits, the Formula paradigm appears to have produced representations of reality that are not being used to any depth, by anyone, clearly for the principle the ontologies being promulgated have no bearing upon the actual models being developed, and tested, by a data scientist most concerned with alternative theories of '''''interaction and evolution''''' within their domains. The core issue is no public domain ontology exists to structure the problems being solved by data scientists, meaning a scientist's use of today's public ontologies is meaningful primarily as an important public service. | ||
Formulaic data structures first emerged as Database Systems and then as Triple Stores. Triple Stores consolidated gargantuan systems of DBMS tables, using ontologies to <u>existentially</u> relate keys inherited from those tables, in hopes of reducing processing costs while increasing processing opportunities. | Formulaic data structures first emerged as Database Systems and then as Triple Stores. Triple Stores consolidated gargantuan systems of DBMS tables, using ontologies to <u>existentially</u> relate keys inherited from those tables, in hopes of reducing processing costs while increasing processing opportunities. | ||
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) introduced | The Resource Description Framework (RDF) introduced a standard model for an "Axiom" (expressed in an RDF Notation) with its ''rdf:Statement'', a "triple" composed of {<i>rdf:Subject, rdf:Predicate, rdf:Object</i>} and essential to logic formulas. The RDF also accommodated its rival meta-model by publishing a standard for <i>rdf:Pair = {rdf:First, rdf:Rest</i>}. Meanwhile the Standard Model for computer science students was made to be a triple relation too, <i>Model-View-Controller</i>, to provide for the growing orientation towards database models, process models and ontology models. | ||
In this context the '''''epsilon operator''''' is introduced by the generic formula, <i>f(x) ε y</i> (where "y" <u>emerges from</u> "f" upon "x"), to identify Emergence Paths pertinent to an Individual or group of Individuals. An Emergence Epistemology is detailed for development of models directly pertinent to ontologists and data scientists alike. | |||
===Referents and References=== | |||
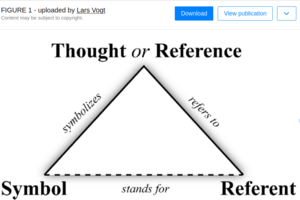
[[Image:Referent.png|right|300px]]This epistemology claims all ontologies must first distinguish their expressions as being references to things that exist, or as the things that exist themselves. All ontologies must define "Referent" and "Reference" as top-level classes of expression. | |||
'''Implications.''' Because language and signs are used to name things, the Sign or Name used is a reference to the concept being described by the Sign or Name. All References thus ''emerge'' as Referents and all referents are thus preceded by instantiation of a reference to a referent. A principle of Emergence applies in this manner: A Reference may exist without a Referent, emerging subsequent as "completed" once the Referent is associated with its Reference. Alternatively constructed, a Reference has not emerged and is "Incomplete", until its association with a Referent. | |||
'''Justification.''' | |||
<blockquote>In semantics and philosophy, a referent is used to establish a connection between a word, phrase, or symbol, and the thing or object it represents or denotes. This allows for clear communication and understanding of the meaning of language. In programming, referent is not commonly used, but it can be used in similar way to establish a connection between a variable or identifier and the object it references.</blockquote> | |||
<hr style='height:4px'/> | <hr style='height:4px'/> | ||
The following material is being rewritten | The following material is being rewritten | ||
Revision as of 23:51, 11 January 2023
The Best Practices Wiki Ontology
An Emergence Epistemology for Modern Ontologies
On the heels of recent evolution in mathematics and astronomy, physics, biology, social sciences, and cognitive research, a new approach to the process of information modeling is needed to support widely common cross-domain requirements, that is, this article proposes a candidate Standard Ontology Model (SOM).
Motivation
Presently ontologies are built using approaches first typified by the Formula Translating System (FORTRAN), and are thus based on essential notions of "data structures" as proxies for operands to an algebraic formula; "routines" being a particular functional formula; and "return values" being the specific knowable output of the formula. The generic formula, y = f(x) (where "y" is equal to "f" upon "x"), exactly maps to the widespread Input-Process-Output model underpinning many methods; it is aptly descriptive to consider the Algebraic Formula the epistemology used to fashion many ontologies.
However if success of ontologies is judged by their fruits, the Formula paradigm appears to have produced representations of reality that are not being used to any depth, by anyone, clearly for the principle the ontologies being promulgated have no bearing upon the actual models being developed, and tested, by a data scientist most concerned with alternative theories of interaction and evolution within their domains. The core issue is no public domain ontology exists to structure the problems being solved by data scientists, meaning a scientist's use of today's public ontologies is meaningful primarily as an important public service.
Formulaic data structures first emerged as Database Systems and then as Triple Stores. Triple Stores consolidated gargantuan systems of DBMS tables, using ontologies to existentially relate keys inherited from those tables, in hopes of reducing processing costs while increasing processing opportunities.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) introduced a standard model for an "Axiom" (expressed in an RDF Notation) with its rdf:Statement, a "triple" composed of {rdf:Subject, rdf:Predicate, rdf:Object} and essential to logic formulas. The RDF also accommodated its rival meta-model by publishing a standard for rdf:Pair = {rdf:First, rdf:Rest}. Meanwhile the Standard Model for computer science students was made to be a triple relation too, Model-View-Controller, to provide for the growing orientation towards database models, process models and ontology models.
In this context the epsilon operator is introduced by the generic formula, f(x) ε y (where "y" emerges from "f" upon "x"), to identify Emergence Paths pertinent to an Individual or group of Individuals. An Emergence Epistemology is detailed for development of models directly pertinent to ontologists and data scientists alike.
Referents and References
This epistemology claims all ontologies must first distinguish their expressions as being references to things that exist, or as the things that exist themselves. All ontologies must define "Referent" and "Reference" as top-level classes of expression.Implications. Because language and signs are used to name things, the Sign or Name used is a reference to the concept being described by the Sign or Name. All References thus emerge as Referents and all referents are thus preceded by instantiation of a reference to a referent. A principle of Emergence applies in this manner: A Reference may exist without a Referent, emerging subsequent as "completed" once the Referent is associated with its Reference. Alternatively constructed, a Reference has not emerged and is "Incomplete", until its association with a Referent.
Justification.
In semantics and philosophy, a referent is used to establish a connection between a word, phrase, or symbol, and the thing or object it represents or denotes. This allows for clear communication and understanding of the meaning of language. In programming, referent is not commonly used, but it can be used in similar way to establish a connection between a variable or identifier and the object it references.
The following material is being rewritten
The Best Practices Wiki Information Model is fundamental to identify (a) semantic tags to markup Best Practices essays (b) semantic classes for Practice, Policy, Procedure and Process models, of prime interest (c) classes for Act, Action, Activity and Task that are the detailed enumerated steps for a "method" that achieves a particularly useful objective.
Related Open Source
mw:Extension:SemanticTasks: provides email task notifications and reminders whose model is centered on assignment of Users to Tasks.
References
- [https:\\kissflow.com/workflow/bpm/business-process/ The Extensive Guide to Business Processes]
- ERP Readiness Series: The Four Core Processes Every Business Should Document
Referents
Partitive Classes
Taxonomic Classes
Topic Annotation (Tags)
Linguistic Classes
Instance Referents
{{Category:Tag <br/>|rdfs:subclassOf=Reference <br/>|name= <br/>|id= <br/>|label= <br/>|path= <br/>|timestamp= <br/>|@category:name }} <!-- {{Hierarchy|Start|2|skos:Concept|https://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/}} {{Hierarchy|End|2|Gender|skos:Concept}} -->
Determiners include articles (a, an, the), cardinal numbers (one, two, three...) and ordinal numbers (first, second, third...), demonstratives (this, that, these, those), partitives (some of, piece of, and others), quantifiers (most, all, and others), difference words (other, another), and possessive determiners (my, your, his, her, its, our, their).